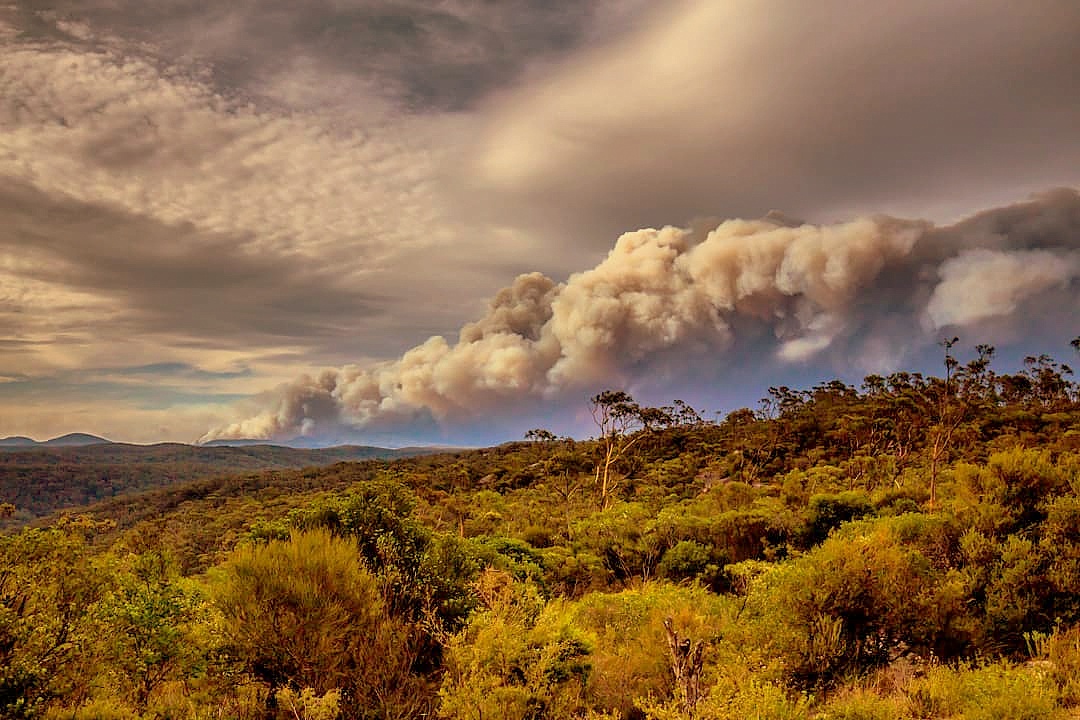
On January 4, 2020, Penrith, an outer Sydney suburb near the Blue Mountains, recorded a searing temperature of 48.9°C—one of the hottest places on Earth that day. This extreme heat demonstrated that climate change is no longer a distant threat on the horizon; Australia is getting hotter, and with rising temperatures come more frequent and intense fire events, such as the devastating Black Summer bushfires.
The 2019/2020 bushfire season began in September 2019 and raged for months, affecting multiple states. The Blue Mountains, with its vast bushland and iconic ecosystems, was particularly hard hit. Fires spread relentlessly through the region, causing widespread environmental, social, and economic damage, leaving a lasting impact on communities.
This blog post examines the far-reaching effects of the Black Summer bushfires on the Blue Mountains, drawing on insights from a report commissioned by exci (formerly Fireball International) from the Australian National University (ANU). We also explore how exci’s AI bushfire detection can reduce future fire risks and help protect this cherished landscape from future devastation.
The Blue Mountains: A Natural Treasure
The Blue Mountains, a UNESCO World Heritage site, are celebrated for their breathtaking cliffs, valleys, and ancient forests. This region is home to many unique species, including the greater glider and the Blue Mountains water skink. In addition to its natural beauty, the Blue Mountains play a vital role in the local economy, particularly through tourism, which attracts visitors for hiking, climbing, and scenic views. The region also provides essential environmental services like carbon storage, water filtration, and wildlife conservation.
However, the 2019-20 bushfires devastated this landscape, incinerating large areas and disrupting ecosystems. The bushfire was ignited by lightning, which spread in all directions, including the northern parts of the Blue Mountains, before eventually spreading south and joining with the rest of the Blue Mountains. It burned for 79 days, leaving a lasting mark on the memories of those who feared its approach and battled its flames. The fire was extinguished ultimately by torrential rains in February 2020. Yet, wildlife suffered heavily, and the local economy, particularly tourism, faced significant setbacks. Understanding the long-term impact of the disaster is crucial for preserving the Blue Mountains and the communities that depend on this remarkable region.
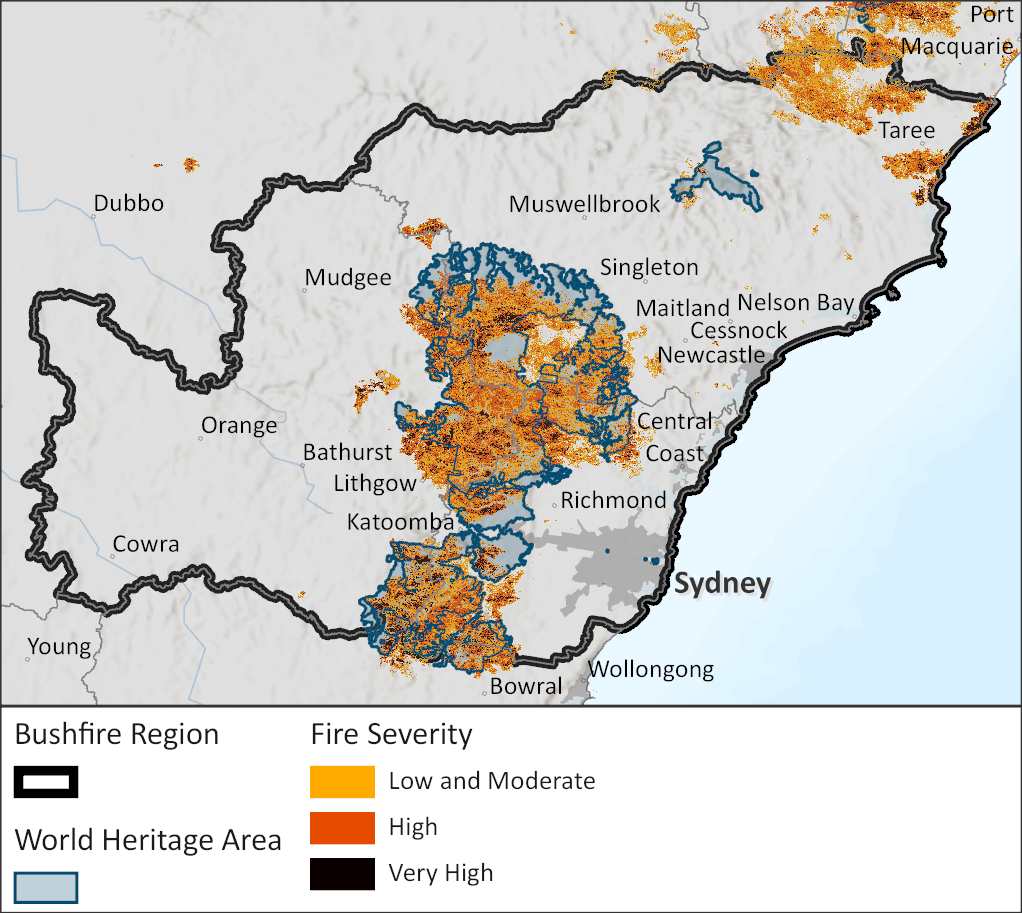 Greater Blue Mountains. Source: https://www.dcceew.gov.au/environment/biodiversity/bushfire-recovery/regional-delivery-program/greater-blue-mountains
Greater Blue Mountains. Source: https://www.dcceew.gov.au/environment/biodiversity/bushfire-recovery/regional-delivery-program/greater-blue-mountains
Environmental Impact: Fragile Ecosystems Under Fire
Biodiversity Loss
The bushfires caused irreversible damage to fragile ecosystems, pushing many endangered species toward extinction. While some fire-adapted plants, such as eucalypts, have begun recovering, sensitive ecosystems—like peat swamps and hanging swamps—may never fully regenerate. This loss of biodiversity threatens the region’s long-term ecological stability.
 Animals impacted by Black Summer bushfires by https://www.dcceew.gov.au/environment/biodiversity/bushfire-recovery/regional-delivery-program/greater-blue-mountains
Animals impacted by Black Summer bushfires by https://www.dcceew.gov.au/environment/biodiversity/bushfire-recovery/regional-delivery-program/greater-blue-mountains
Soil and Water Quality
Fires strip vegetation and organic matter, leaving bare soil vulnerable to erosion. Following the Black Summer bushfires, heavy rains caused flash floods, severely damaged forest roads, and washed ash and silt into waterways, disrupting aquatic ecosystems and degrading water quality.
 Bushfire affected waterways. Source: https://www2.environment.nsw.gov.au/topics/water/estuaries/estuaries-research/bushfire-affected-waterways/how-bushfires-impact-water-quality
Bushfire affected waterways. Source: https://www2.environment.nsw.gov.au/topics/water/estuaries/estuaries-research/bushfire-affected-waterways/how-bushfires-impact-water-quality
Economic Aftermath: Tourism, Agriculture, and Infrastructure
The Black Summer bushfires inflicted severe economic damage, particularly on the Blue Mountains’ tourism, agriculture, and infrastructure.
- Tourism: This sector, a vital pillar of the local economy, was hit the hardest. Popular attractions were closed, and hotels, tours, and businesses suffered from cancellations. Recovery was slow, with visitor numbers suppressed by safety concerns and damaged landscapes. The tourism sector lost 2,600 jobs, causing a turnover loss of $560 million.
- Agriculture: Farms and vineyards also experienced significant losses. Destroyed crops, livestock deaths, and disrupted operations posed immediate challenges, while rebuilding facilities and managing fire-damaged soil introduced long-term hurdles. Agricultural losses across affected regions in Australia reached an estimated $5 billion.
- Infrastructure: The fires destroyed homes and damaged powerlines, roads, and communication systems, leading to costly repairs. The overall economic impact was staggering, with a reduction in Australia’s GDP by $4.6 billion, particularly affecting New South Wales and Victoria.
The combined impact of tourism loss, agricultural damage, and infrastructure rebuilding continues to shape the economic landscape of the Blue Mountains. Innovative approaches to fire management are essential for minimising future economic disruptions.
Social Impact of the Black Summer Bushfires on the Blue Mountains Communities
Displacement and Emotional Loss
The Black Summer bushfires deeply affected the people of the Blue Mountains. Thousands of residents were forced to evacuate, and many lost everything to the flames. Beyond the destruction of property, families lost cherished memories, leaving emotional scars that linger long after the fires. For those displaced, the emotional burden of physically and mentally rebuilding has been overwhelming.
Disruption of Daily Life
The fires disrupted the rhythm of everyday life. Schools and businesses shut down temporarily, and community events were cancelled. Many residents found themselves in emergency shelters, while others leaned on friends, family, or neighbours for support. This sudden upheaval strained relationships and placed immense pressure on local resources.
Mental and Physical Health Challenges
The emotional toll of the fires was immense, with many residents experiencing trauma, anxiety, and grief. The uncertainty and exhaustion of repeated evacuations and recovery efforts wore down families. Prolonged exposure to smoke also caused respiratory issues, adding to the health challenges and increasing demand for healthcare services.
Community Strength and Resilience
Despite these hardships, the fires revealed the resilience of the Blue Mountains communities. Neighbours banded together to share food, shelter, and emotional comfort. Volunteers and emergency responders selflessly put themselves at risk to protect others. These acts of solidarity highlighted the strength within the community but also emphasised the need for ongoing mental health services and structured recovery programs.
Ongoing Recovery and Preparedness
Rebuilding remains a long and complex journey for many families. Issues like unresolved insurance claims, housing repairs, and financial instability continue to create challenges. Lingering fears about future bushfires further complicate recovery efforts.
However, the shared experience of the Black Summer fires has sparked critical conversations about fire preparedness and safety. There is now a growing recognition of the importance of early AI wildfire detection systems to mitigate future risks. Solutions like exci’s AI-powered technology offer a vital tool to help communities respond more effectively, reducing the impact of future fires.
The Urgent Need for AI Bushfire Detection
Economic Savings Through Early Detection
The 2019-20 bushfires underscored the critical need for early fire detection to minimize economic, environmental, and social impacts. To assess the financial benefits of early detection, exci (formerly Fireball.International) commissioned the Australian National University (ANU) to conduct a study titled “Measuring the Economic Impact of Early Bushfire Detection.”
The report projects bushfire-related economic costs over the next 30 years (2020–2049) and highlights how investing in early detection systems—capable of responding within 30 minutes—can significantly reduce these costs.
Key Findings from the ANU Report
- Projected Costs: Bushfires could cost Australia $2.2 billion annually or $1.2 billion per year in Net Present Value (NPV) over the next 30 years under current climate change scenarios.
- Economic Savings from Early Detection: Investments in early fire detection systems could reduce costs by up to $8.2 billion (NPV), even with conservative assumptions.
- Rapid Response: Faster detection enables firefighting teams to respond before fires escalate, preventing small ignitions from becoming catastrophic events, especially in remote areas.
 Economic costs of bushfires. Source: https://csrm.cass.anu.edu.au/sites/default/files/docs/2020/9/Measuring the economic impact of early bushfire detection.pdf
Economic costs of bushfires. Source: https://csrm.cass.anu.edu.au/sites/default/files/docs/2020/9/Measuring the economic impact of early bushfire detection.pdf
Proactive Investment in Early Fire Detection
The report calls for a shift from post-disaster recovery to proactive investment in early fire detection. exci’s AI wildfire detection technology goes beyond issuing early alerts— it offers real-time monitoring and provides customers with direct camera access and control when needed. This capability significantly enhances firefighting efforts and improves response strategies, ensuring a faster, more effective approach to managing wildfires.
The financial and environmental advantages of exci’s AI-powered bushfire detection system make it an essential tool for effective wildfire management in a rapidly changing climate.
exci’s AI Wildfire Detection: A Game-Changer
exci’s AI-powered wildfire detection system leverages advanced deep learning algorithms to detect fires at their earliest stages. By analysing data from ground-based cameras and satellites, the system identifies smoke and heat signatures in real-time. Forest fires as small as a garden shed are detected within minutes, with almost zero false positives.
When a fire is detected, exci’s system sends real-time alerts to firefighting teams, enabling rapid response. Live camera feeds provide critical situational awareness, empowering emergency services to act swiftly and contain fires before they spread. This AI fire detection technology provides a vital edge in reducing fire damage, helping forest managers, emergency responders, and local authorities protect lives and property.
 exci’s AI wildfire detection technology
exci’s AI wildfire detection technology
Creating a Safer Future with Early Wildfire Detection
Bushfires are an inherent part of Australia’s landscape, but their frequency and intensity are increasing due to climate change. The devastation caused by the Black Summer bushfires highlights the need for innovative solutions like exci’s AI-powered wildfire detection.
The ANU report commissioned by exci demonstrates that early fire detection not only saves lives and ecosystems but also offers significant economic benefits. With exci’s cutting-edge technology, small forest fires can be identified before they escalate, minimising the risks to communities, biodiversity, and infrastructure.
While it may not be possible to eliminate bushfires entirely, AI-driven early forest fire detection offers a powerful tool to mitigate their impacts. Investing in these technologies today will create a more resilient future, safeguarding Australia’s natural treasures and communities in an increasingly volatile climate.
by Gabrielle Tylor
16 October 2024
exci – Smoke Alarm for the Bush
AI Wildfire & Bushfire Detection Technology
Don’t let Hazardous Events become Catastrophic!
Contact our friendly team today for a comprehensive demonstration of exci’s system and discover how it can protect your assets while also protecting your community.
email: info@exci.ai
International Phone: +61 458 594 554
Visit our website at https://www.exci.ai/ to learn more and take the first step towards a safer and more resilient future.

